what is unique about the pancreas compared to the other endocrine glands

What is Endocrine Arrangement?
Hormones are chemicals that bear upon a lot of the bodily functions ranging from hunger, reproduction and growth to much more than complicated functions like human being emotions and behaviour. These hormones are produced in our body through nine primary glands and these glands, along with other organs that provide auxiliary functions make up the endocrine organization.
Let us have a detailed await at the endocrine arrangement notes and explore the major endocrine glands in the human torso.
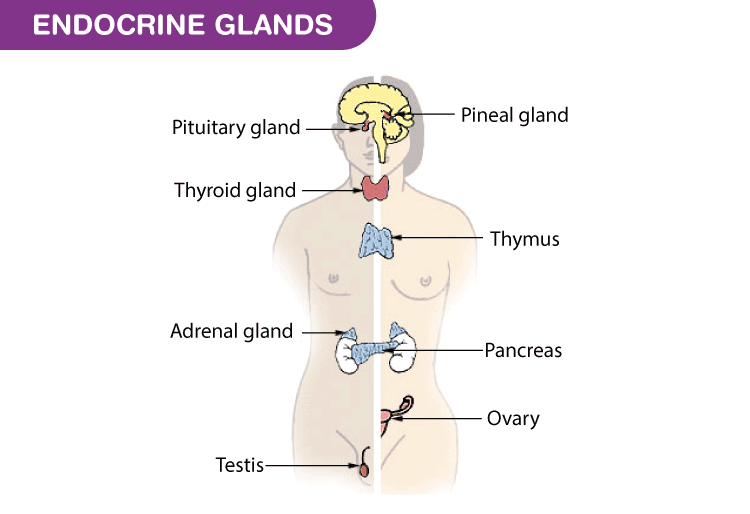
Unlike exocrine glands(sweat, salivary), endocrine glands secrete their respective substances directly into the bloodstream rather than through a duct. These endocrine glands vest to the body'due south command system and they produce hormones which help to regulate the functions of cells and tissues. Some glands are specific to either male (testes) or female person (ovaries)
Major Endocrine Glands
Pituitary gland
Enclosed deep within the skull, the pituitary gland is the size of a pea. It hangs on a stem at the base of operations of the brain. It consists of an anterior portion that produces hormones and a posterior portion that has many neural links. This gland is regarded as the main gland as it controls the functions of all the other glands (such as the adrenal, thyroid glands) in the endocrine system. The pituitary gland stimulates the adrenal gland to secrete cortisol, a steroid hormone controls a range of activities from controlling the body'south metabolism to stimulating blood pressure. The pituitary gland as well secretes prolactin, which stimulates the production of milk.
Thyroid gland
The thyroid glands can be plant at the front of the neck. Information technology sits depression in the throat, between the windpipe. Brown blood-red, it has blood vessels coursing through it. Information technology secretes hormones that are collectively called thyroid hormones. The virtually prominent are T3 and T4, which influence the body'due south rate of metabolism.
Parathyroid glands
The parathyroid glands consist of four small glands that are located behind the thyroids in the neck. They influence the calcium levels in the trunk past producing a hormone called Parathyroid Hormone. Sometimes, when the gland produces excess parathyroid hormones, it can have negative effects such as breakable bones and kidney stones.
Adrenal glands
The adrenal glands sit atop the kidneys and are no larger than a walnut. These glands produce over 150 hormones that regulate different functions in the torso. The most well known is Adrenaline, which triggers the flight or fight response. In other words, this is a stress hormone that helps the organism to either confront a dangerous situation or to avoid it altogether. It does this past:
- Increasing blood sugar levels
- Increasing the blood supply to the muscles, particularly to the limbs.
- Dilating the pupils
- Increasing the heart rate
- Tightening the jaw muscles.
Pancreas
The pancreas is exocrine as well as an endocrine gland that sits behind the stomach. It is roughly 6 inches long and rather flat. The pancreas has two master roles to play:
- Producing digestive enzymes
- Producing hormones such as insulin and glucagon.
Insulin is produced past the β cells in the pancreas and information technology helps in regulating the blood glucose levels in the body from getting as well high. As we are all aware, the lack of insulin causes blazon 1 and blazon 2 diabetes. The hormone glucagon is produced past α cells of the pancreas and it helps the body to forbid the glucose levels from dropping too low. Lack of glucagon leads to hypoglycemia. Some other key difference between the two is insulin becomes agile when the blood glucose levels are high, and glucagon become active just when blood glucose levels are low.
Gonads
Some glands are specific to males or females. For example, the ovaries are specific to females and are located in the pelvic cavity. While the testes are specific to males. Ovaries produce estrogen that is important for reproduction and female sexual practice characteristics. Testes produce testosterone that is responsible for male sexual activity characteristics. As well, it results in increased muscle mass and body hair.
Pineal gland
The pineal gland is located between the 2 halves of the brain. It was too known as the "3rd center" for virtually of history due to its location in the brain and its connection with light.
It produces a hormone known as melatonin which influences the body'due south internal clock. Also known equally the Cyclic Rhythm, it influences the body's sleep/wake cycle. Its effects are not actually noticeable unless the individual is sleep-deprived. Factors such as jet lag, or working the dark shift has a more noticeable event on an individual because Cyclic rhythm tends to coincide with the twenty-four hours and nighttime cycle. That'due south why individuals who work during the night find it hard to fall asleep during the day, and consequently stay awake for the next night.
Recommended Video:

Register at BYJU'Southward for endocrine system notes. Refer to these notes for reference.
Source: https://byjus.com/biology/endocrine-glands/
0 Response to "what is unique about the pancreas compared to the other endocrine glands"
Post a Comment